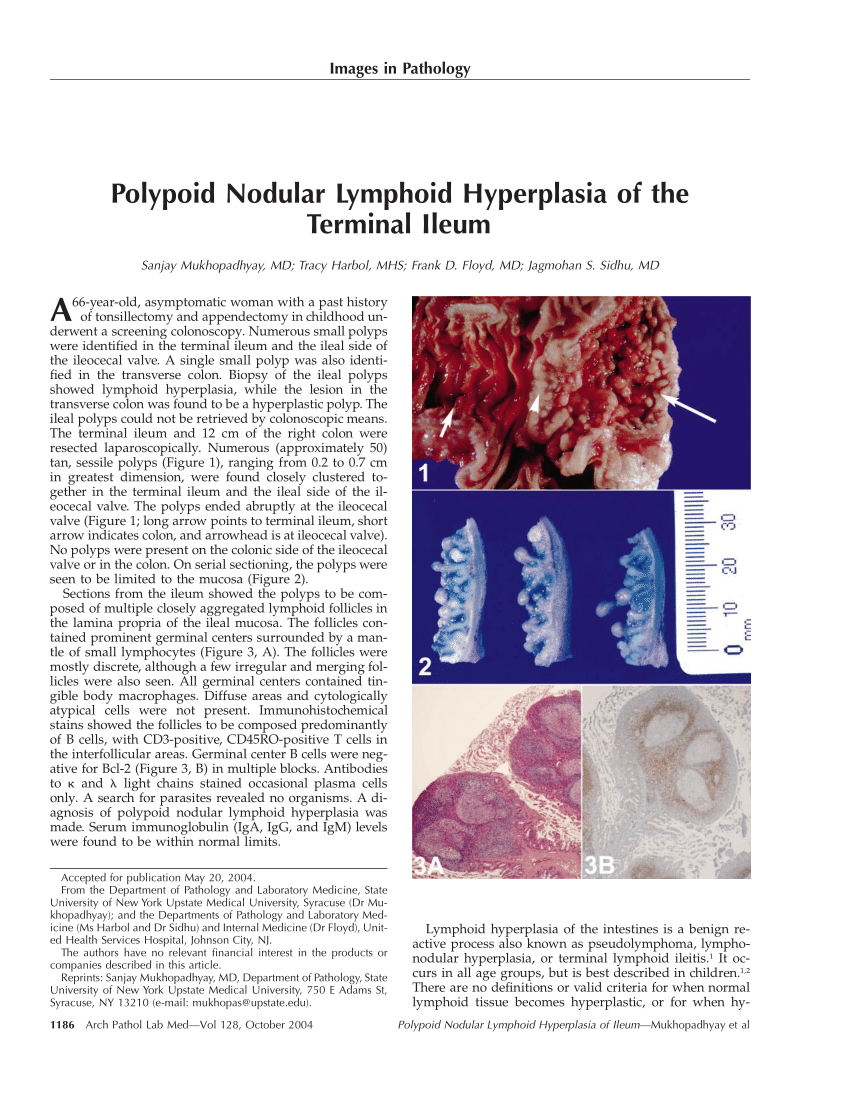
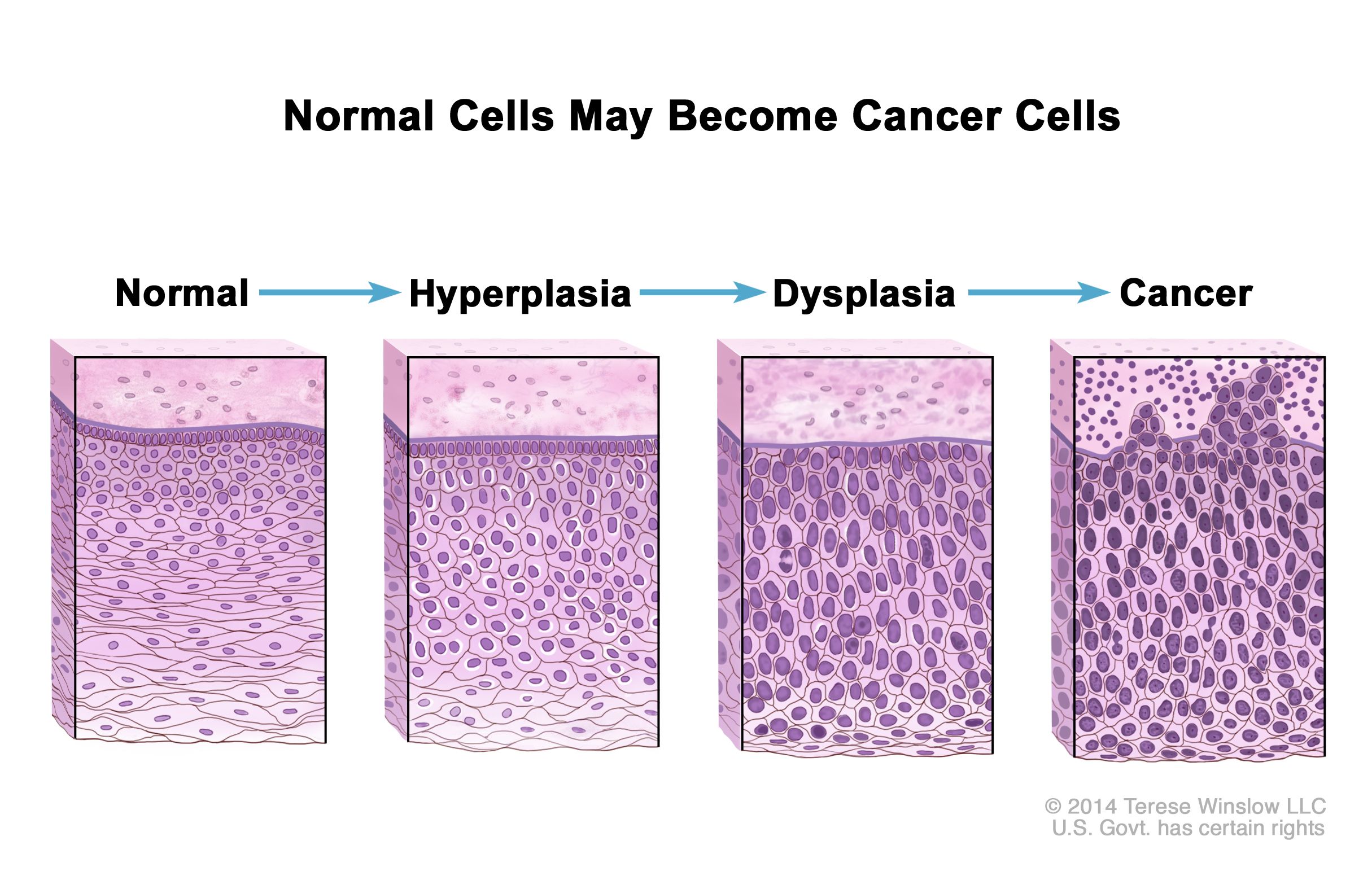
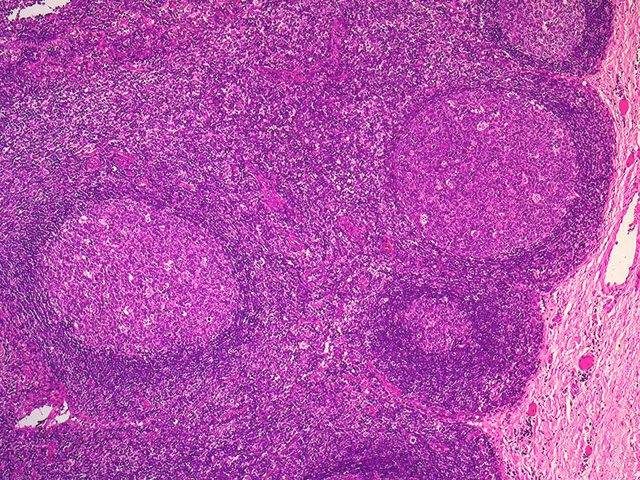
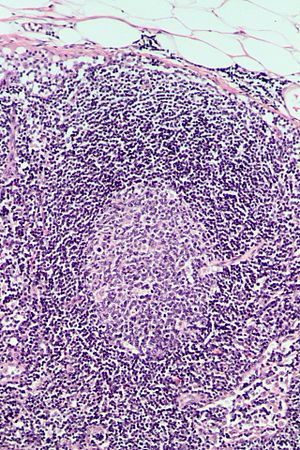
Definition Benign Lymphoid Hyperplasia
Lymphoid hyperplasia or lymphoid hypertrophy can occur in the presence of bacteria a virus or anomalous tissue growth the increase in thenumber of lymphocytes commonly associated with the body s immune response can be initiated by a.
Definition benign lymphoid hyperplasia. Lymphoid hyperplasia may also occur as a secondary component in certain disorders such as crohn s disease and may sometimes cause difficulty in diagnosis. Histological features include distention or engorgement of both subscapular and inatraparenchymal sinuses by benign histiocytes which may be hemophagocytic. 2 benign lymphoid hyperplasia patients report moderate depressed mood 40 0 benign lymphoid hyperplasia patients report mild depressed mood 0 1 a benign lymphoid hyperplasia patient reports no depressed mood 20 what people are taking for it sertraline.
Can someone please tell me what in human terms this means. Posted by strong enough 2011 strongenough2011 aug 10 2011. Nodular lymphoid hyperplasia nlh is a rare benign condition that is characterized by diffuse hyperplasia of the lymphoid follicles of the gastrointestinal tract git.
Follicular hyperplasia of the lymph nodes in the neck is diagnosed as a characteristic symptom of angiofollikular lymphoid hyperplasia or castleman s disease. Lymphoid hyperplasia is the swelling of lymph tissue due to an accelerated increase of lymphocytes when the immune system perceives a threat to the body. Benign reactive lymphoid hyperplasia.
Sinus hyperplasia is the preferential stimulation of the histiocytic tissues macrophage compartment. Sinus hyperplasia may be associated with non hematolymphoid malignancy. May be significant in adults.
During endoscopy nlh appears as multiple or occasionally innumerable nodules measuring a few millimeters in diameter. Furthermore cell growth stops when the stimulus is removed in hyperplasia while neoplasia contains continuous cell growth. Epidemiology lymphadenopathies manifested clinically by the enlargement of lymph nodes are a common.
Clinical findings generally asymptomatic. Strong enough 2011 strongenough2011. A reactive nonspecific process to various pathogens e g salmonella yersinia mycobacterium or immune mediated insults as occurs in inflammatory bowel disease celiac disease and peptic disease.